Review
- 2020/08/05
- 2021/01/29
- 2024-08-06 08:00
[!Summary] redux https://github.com/reduxjs/redux redux-toolkit(RTK) https://github.com/reduxjs/redux-toolkit new react-redux https://github.com/reduxjs/react-redux
[!info]
- 架构
- 运行流程
- 中间件运行机制
一、Introduction #
Redux is a JS library for predictable and maintainable global state management.
Redux is really:
- A single store containing “global” state
- Dispatching plain object actions to the store when something happens in the app
- Pure reducer functions looking at those actions and returning immutably updated state
Redux is a pattern and library for managing and updating application state, using events called “actions". It serves as a centralized store for state that needs to be used across your entire application, with rules ensuring that the state can only be updated in a predictable fashion.
Redux是一个模式和库,使用被称为“actions”的事件,来管理和更新应用程序的全局state。被当作全局集中的state存储,用规则确保只能被可预测的方式更新。
Data flows through a Redux app: “one-way data flow”
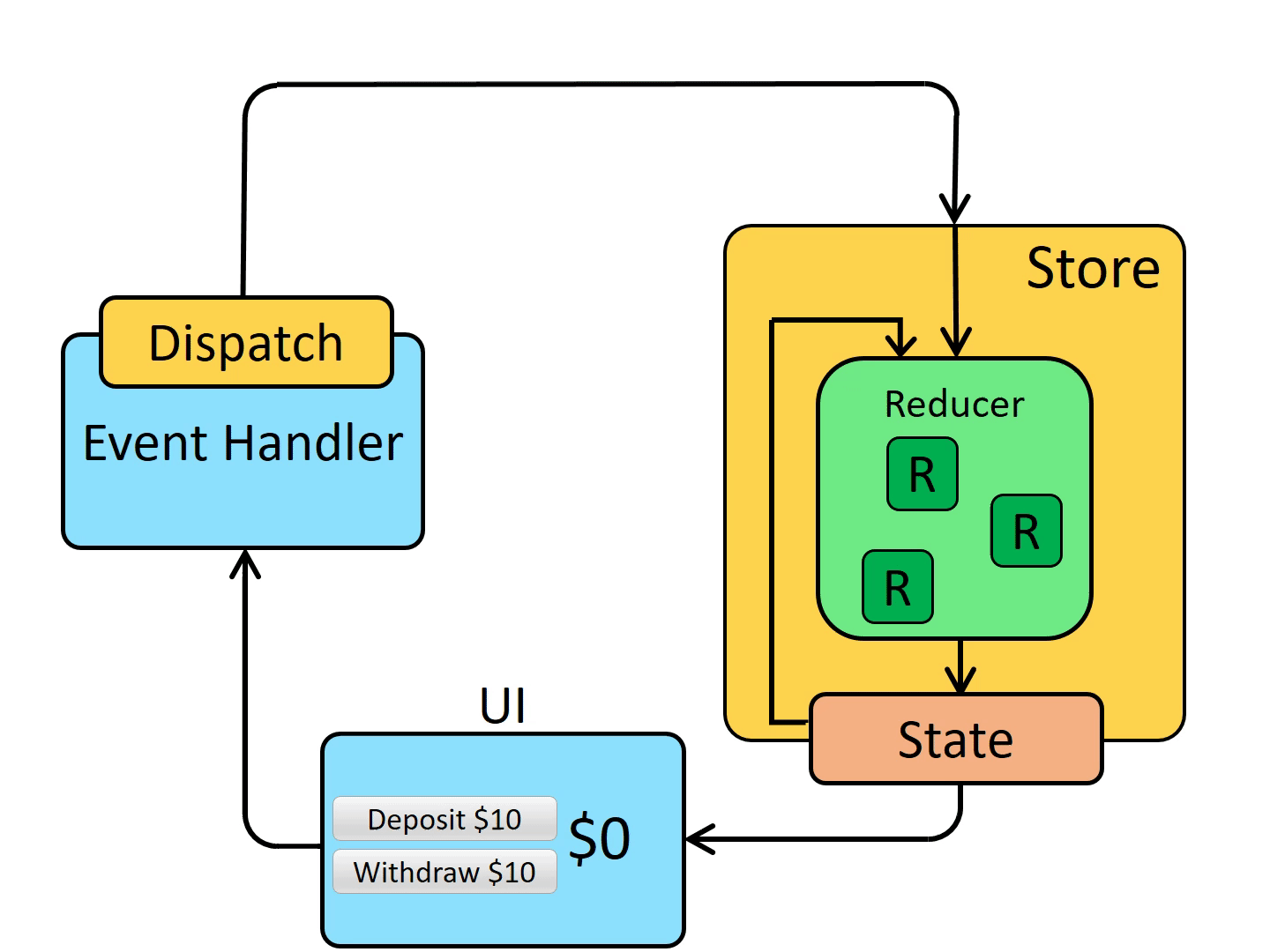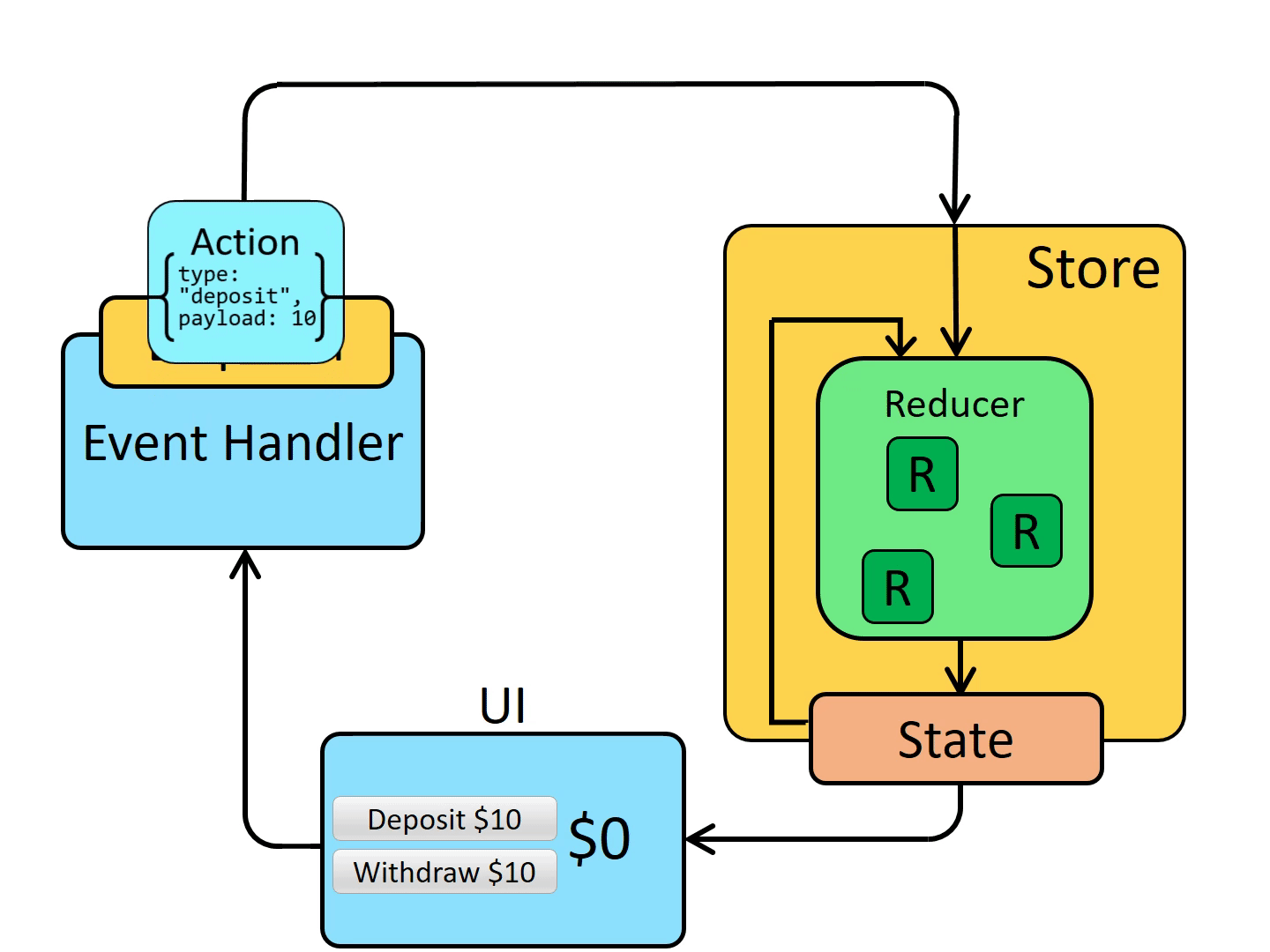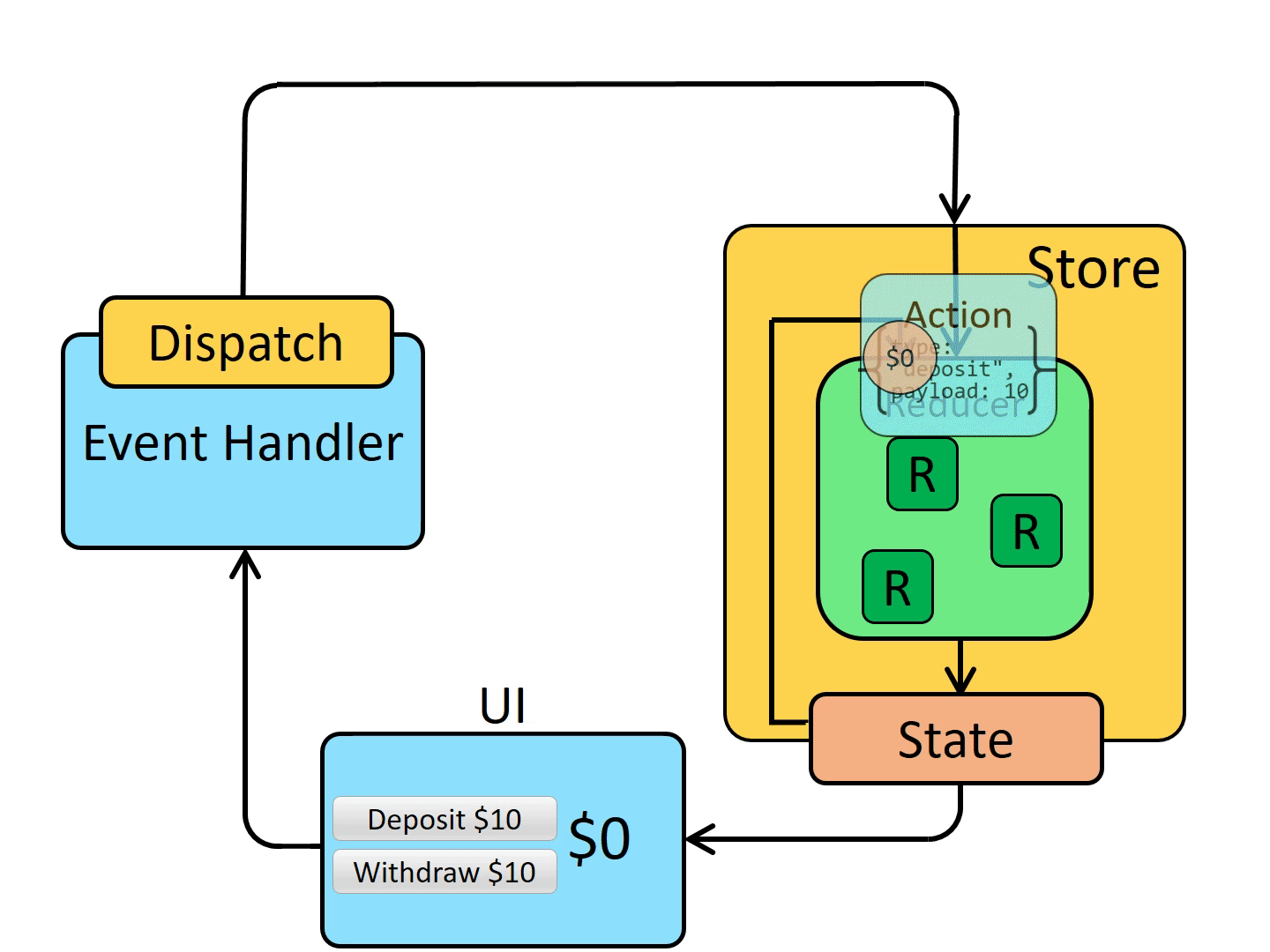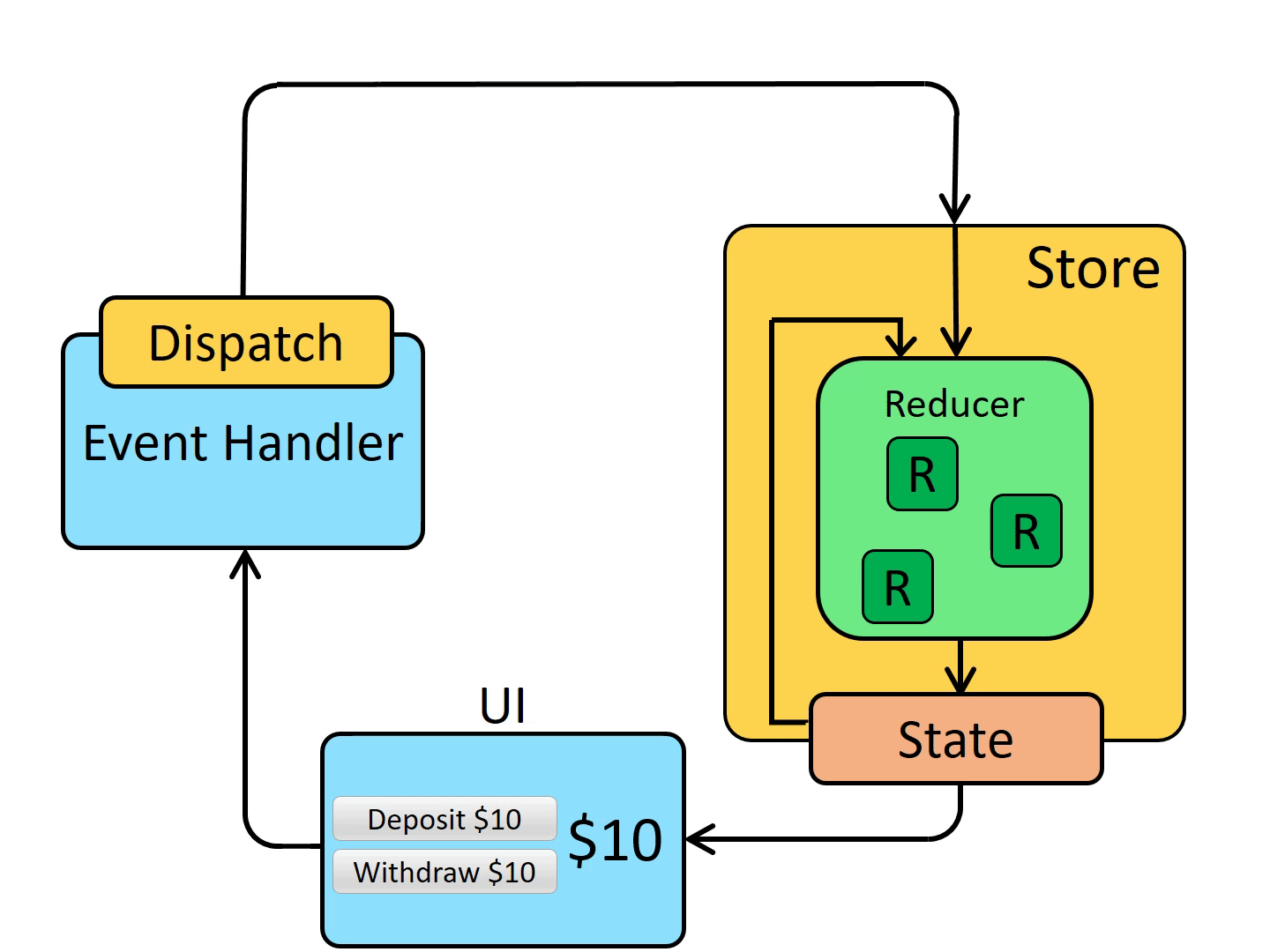
The Redux core is a very small and deliberately unopinionated library. It provides a few small API primitives:
createStoreto actually create a Redux storecombineReducersto combine multiple slice reducers into a single larger reducerapplyMiddlewareto combine multiple middleware into a store enhancercomposeto combine multiple store enhancers into a single store enhancer
Why you might want to use it? #
The patterns and tools provided by Redux make it easier to understand when, where, why, and how the state in your application is being updated, and how your application logic will behave when those changes occur.
Redux is more useful when:
- You have large amounts of application state that are needed in many places in the app
- The app state is updated frequently over time
- The logic to update that state may be complex
- The app has a medium or large-sized codebase, and might be worked on by many people
Key Redux terms and concepts #
State #
In redux, the state is a centralised object tree containing the information used by the application. The only way to modify the state is by dispatching actions.
Actions #
An action is a plain JavaScript object that has a type field. You can think of an action as an event that describes something that happened in the application.
An action creator is a function that creates and returns an action object.
Reducers #
A reducer is a function that receives the current state and an action object, decides how to update the state if necessary, and returns the new state: (state, action) => newState.
Store #
The current Redux application state lives in an object called the store .
Dispatch #
The Redux store has a method called dispatch. The only way to update the state is to call store.dispatch() and pass in an action object.
Selectors #
Selectors are functions that know how to extract specific pieces of information from a store state value.
Subscribe #
react-redux #
Redux middleware #
Redux Middleware #
- redux-thunk
- redux-promise
- [[Redux-Saga]]
- redux-observable
- …
redux-thunk & redux-saga & redux-primise & redux-observable Async action creators are especially convenient for server rendering. You can create a store, dispatch a single async action creator that dispatches other async action creators to fetch data for a whole section of your app, and only render after the Promise it returns, completes. Then your store will already be hydrated with the state you need before rendering.
- You can use redux-promise or redux-promise-middleware to dispatch Promises instead of functions.
- You can use redux-observable to dispatch Observables.
- You can use the redux-saga middleware to build more complex asynchronous actions.
- You can use the redux-pack middleware to dispatch promise-based asynchronous actions.
Asynchronous middleware like redux-thunk or redux-promise wraps the store’s dispatch() method and allows you to dispatch something other than actions, for example, functions or Promises. Any middleware you use can then intercept anything you dispatch, and in turn, can pass actions to the next middleware in the chain. For example, a Promise middleware can intercept Promises and dispatch a pair of begin/end actions asynchronously in response to each Promise.
redux生态 reduxsauce < https://github.com/jkeam/reduxsauce>
Reference #
- redux-promise-middleware: https://github.com/pburtchaell/redux-promise-middleware
- redux-saga: https://github.com/redux-saga/redux-saga/
- redux-observable: https://github.com/redux-observable/redux-observable/
- redux-promise: https://github.com/redux-utilities/redux-promise
- redux-thunk: https://github.com/reduxjs/redux-thunk
- redux-loop: https://github.com/redux-loop/redux-loop
- thunkvspromisevssaga: https://juejin.cn/post/6844903504427892750
- redux-saga漫谈: https://www.yuque.com/lovesueee/blog/redux-saga#apyvym
- Redux 4ways
- Redux Middleware Comparison: Thunk, Sagas, Observable & Loop
- A beginners guide to setting up redux-saga with Typescript using reduxsauce