Shell script #
Review
- 2019/12/25
- 2020/04/16
- 2024/06/20
脚本头部规范 #
#!/bin/bash
set -euo pipefail
trap "echo 'error: Script failed: see failed command above'" ERR变量和字符串操作 #
变量定义和使用 #
# 定义变量
name="John"
age=25
# 使用变量
echo $name
echo ${name} # 推荐使用这种方式,更清晰
# 只读变量
readonly PI=3.14159
# 删除变量
unset name字符串操作 #
# 字符串长度
str="Hello World"
echo ${#str} # 输出 11
# 字符串截取
echo ${str:0:5} # 输出 Hello
echo ${str:6} # 输出 World
# 字符串替换
echo ${str/World/Shell} # 输出 Hello Shell条件判断 #
if 语句 #
if [ condition ]; then
commands
elif [ condition ]; then
commands
else
commands
fi条件测试 #
# 文件测试
[ -f file ] # 文件存在
[ -d dir ] # 目录存在
[ -r file ] # 文件可读
[ -w file ] # 文件可写
[ -x file ] # 文件可执行
# 字符串比较
[ "$str1" = "$str2" ] # 字符串相等
[ "$str1" != "$str2" ] # 字符串不等
[ -z "$str" ] # 字符串为空
[ -n "$str" ] # 字符串非空
# 数值比较
[ $num1 -eq $num2 ] # 等于
[ $num1 -ne $num2 ] # 不等于
[ $num1 -gt $num2 ] # 大于
[ $num1 -lt $num2 ] # 小于
[ $num1 -ge $num2 ] # 大于等于
[ $num1 -le $num2 ] # 小于等于循环 #
for 循环 #
# 基本形式
for i in 1 2 3 4 5; do
echo $i
done
# 范围形式
for i in {1..5}; do
echo $i
done
# C语言风格
for ((i=1; i<=5; i++)); do
echo $i
donewhile 循环 #
# 基本形式
count=1
while [ $count -le 5 ]; do
echo $count
count=$((count + 1))
done
# 无限循环
while true; do
echo "Running..."
sleep 1
doneuntil 循环 #
count=1
until [ $count -gt 5 ]; do
echo $count
count=$((count + 1))
done函数 #
# 定义函数
function_name() {
local var1=$1 # 局部变量
local var2=$2
# 函数体
return 0 # 返回值
}
# 调用函数
function_name arg1 arg2
# 获取函数返回值
result=$?数组 #
# 定义数组
array=(1 2 3 4 5)
# 访问数组元素
echo ${array[0]} # 第一个元素
echo ${array[@]} # 所有元素
echo ${#array[@]} # 数组长度
# 遍历数组
for i in "${array[@]}"; do
echo $i
done添加颜色输出 #
echo -e "\e[COLORmSample Text\e[0m"| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-e | Enable interpretation of backslash escapes |
\e[ | Begin the color modifications |
COLORm | Color Code + ’m’ at the end |
\e[0m | End the color modifications |
echo -e "\e[31mRed Text\e[0m"# info=\e[0;36m
# warning=\e[;33m
# success=\e[0;32m
# error=\e[0;31m
# nc=\e[0m参考
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5947742/how-to-change-the-output-color-of-echo-in-linux
- https://www.shellhacks.com/bash-colors/
查找双字节文字 #
perl -ane '{ if(m/[[:^ascii:]]/) { print } }'常用 Linux Commands #
查进程有两个命令
ps -efps auxkill -9 processId杀掉某个进程lsof -i:4000查看某个端口详细的信息:
top 命令查看进程的状态,其中有个 load average 可能不是那么好理解,下面来解释一下:
load average:在特定时间间隔内运行队列中(在CPU上运行或者等待运行多少进程)的平均进程数。
load average 有三个值,分别代表:1分钟、5分钟、15分钟内运行进程队列中的平均进程数量。
- 正在运行的进程 + 准备好等待运行的进程 在特定时间内(1分钟,5分钟,10分钟)的平均进程数
Linux进程可以分为三个状态:
- 阻塞进程
- 可运行的进程
- 正在运行的进程
比如现在系统有2个正在运行的进程,3个可运行进程,那么系统的load就是5,load average 就是一定时间内的load数量均值。
$# vs $@ vs $?
#
Example:
file: test.sh
#! /bin/sh
echo '$#' $#
echo '$@' $@
echo '$?' $?If you run the above script as
./test.sh 1 2 3You get output:
$# 3
$@ 1 2 3
$? 0You passed 3 parameters to your script.
$# = number of arguments. Answer is 3
$@ = what parameters were passed. Answer is 1 2 3
$? = was last command successful. Answer is 0 which means 'yes'Operator #
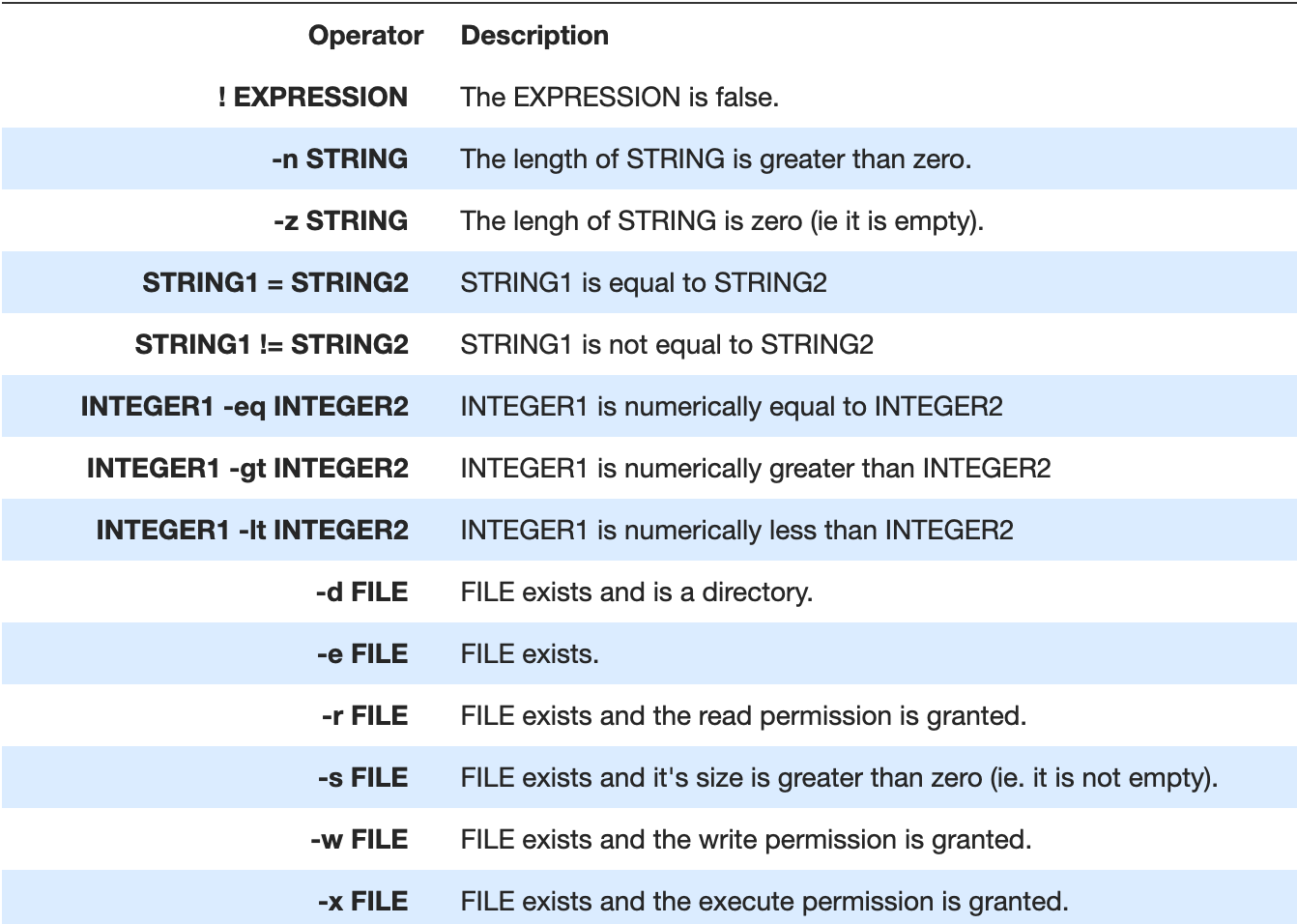
awk #
查找package.json的版本号
awk -F\" '/"version": "([a-zA-Z0-9\.]+)"(,)?$/{print $4}' ./package.json调试技巧 #
# 启用调试模式
set -x # 显示执行的命令
set +x # 关闭调试模式
# 使用 trap 捕获信号
trap 'echo "Script interrupted"; exit' INT TERM
# 使用 -v 选项显示脚本执行过程
bash -v script.sh
# 使用 -n 选项检查语法错误
bash -n script.sh最佳实践 #
- 使用
set -euo pipefail确保脚本在出错时立即退出 - 使用
trap处理错误和清理工作 - 使用
local声明局部变量 - 使用
readonly声明只读变量 - 使用
[[ ]]而不是[ ]进行条件测试 - 使用
$()而不是反引号进行命令替换 - 使用双引号引用变量和字符串
- 使用
printf而不是echo进行格式化输出 - 使用
mktemp创建临时文件 - 使用
trap清理临时文件
Reference #
- https://github.com/wangdoc/bash-tutorial
- https://github.com/jlevy/the-art-of-command-line/blob/master/README-zh.md
- https://devhints.io/bash
- Shellcheck https://github.com/koalaman/shellcheck
- awesome shell https://github.com/alebcay/awesome-shell
- Filenames and Pathnames in Shell: How to do it Correctly https://dwheeler.com/essays/filenames-in-shell.html
- https://likegeeks.com/regex-tutorial-linux/
- http://einverne.github.io/post/2018/01/awk.html
- https://likegeeks.com/awk-command/#Using-Variables
- https://www.tecmint.com/learn-use-awk-special-patterns-begin-and-end/
- http://www.grymoire.com/Unix/Awk.html
- https://www.shellcheck.net/
- https://mywiki.wooledge.org/BashGuide
- https://tldp.org/LDP/abs/html/