Review
- 2023-07-07 07:23
- 2024-09-28
一、Introduction #
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the foundation of the World Wide Web, and is used to load webpages using hypertext links. HTTP is an application layer protocol designed to transfer information between networked devices and runs on top of other layers of the network protocol stack. A typical flow over HTTP involves a client machine making a request to a server, which then sends a response message.
HTTP operates on a stateless, request-response model. This means that each request is independent of the others, making it a fast and efficient way of transmitting data.
However, HTTP has one significant drawback — it’s not secure. Since it’s transmitted in plain text, anyone intercepting the traffic can easily read the content of the messages. This makes HTTP unsuitable for sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers.
HTTPS #
To address the security concerns of HTTP, HTTPS was introduced as a secure alternative. HTTPS uses encryption to ensure that data transmitted between the client and server is confidential and cannot be deciphered by a third-party.
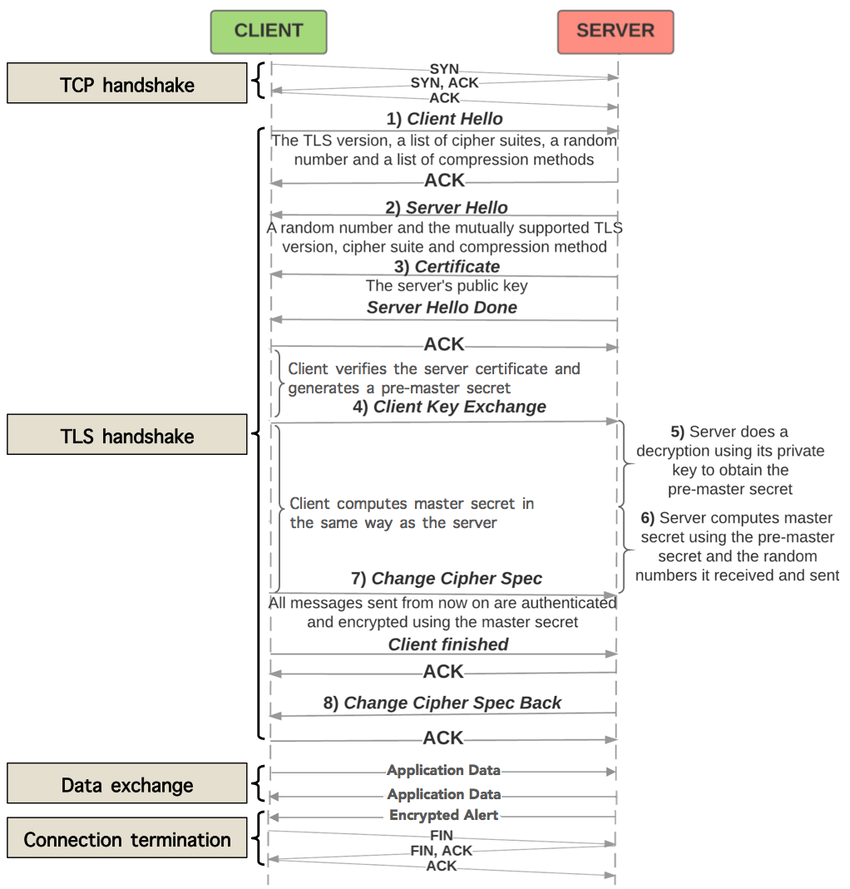
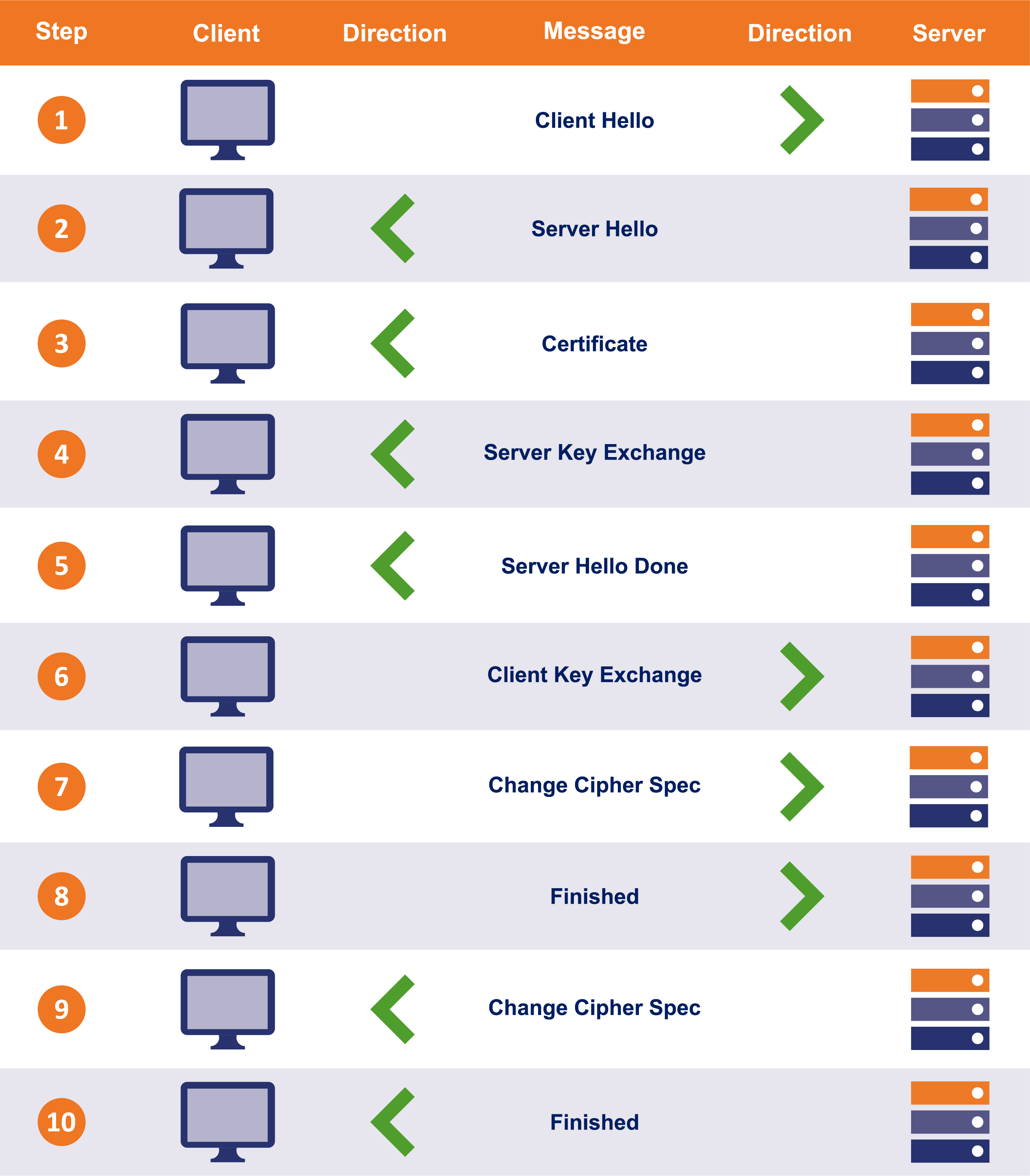
HTTPS uses either SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) to encrypt data. These cryptographic protocols provide end-to-end security, ensuring data integrity and authentication. When you visit a website with HTTPS, you can be confident that your information is being securely transmitted.
To implement HTTPS, websites need to obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This certificate authenticates the website’s identity and helps establish a secure connection between the client and server.
TLS 1.2 流程